MACCON specializes in the development and supply of switched reluctance (SR) and synchronous reluctance (SyR) motors.
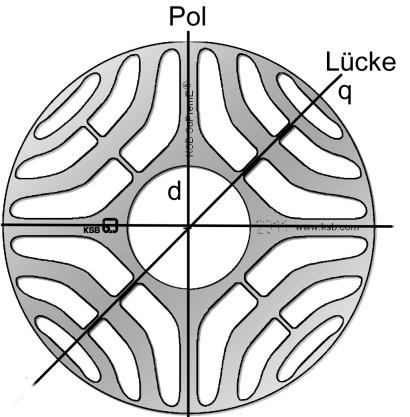
Reluctance motors are based on the magnetic reluctance principle, which utilizes the magnetic attraction of an electromagnet to iron. SR motors are characterized by distinct stator and rotor poles. On the other hand, SyR motors have a traditional stator while the rotor is round and possesses an inner structure with magnetic paths of varying reluctance symmetrically distributed around the rotor.
The SR motor has a different number of stator and rotor poles. Both the rotor and the stator are laminated to reduce eddy current losses. Each stator pole has an excitation coil. The opposing poles are electrically connected to form the North-South pole pair of a phase. The phases are controlled by two electronic switches in a specific current direction pattern. Continuous torque is achieved by correctly switching the phase currents with respect to the angle.
The following is an overview of the key features of switched reluctance motors and synchronous reluctance motors:
Switched Reluctance Motors (SR Motors):
- Distinct stator and rotor poles
- Laminated construction of rotor and stator to reduce eddy current losses
- Each stator pole has an excitation coil
- Opposing poles are electrically connected to form North-South pole pairs of a phase
- Phases are controlled by electronic switches in a specific current direction pattern
- Proper sequential switching of phase currents leads to continuous torque
Synchronous Reluctance Motors (SyR Motors):
- Traditional stator and a round rotor with an inner structure
- The inner rotor structure provides magnetic paths of varying reluctance symmetrically distributed around the rotor
- Laminated construction of the rotor to reduce eddy current losses
- The stator is controlled by excitation coils
- A continuous torque is generated through the specific arrangement of reluctance paths in the rotor
Both types of motors offer specific advantages and characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Switched reluctance motors provide easy control and high torque at low speeds. On the other hand, synchronous reluctance motors offer high efficiency and a wider speed range.
MACCON has extensive experience in the development and optimization of switched reluctance and synchronous reluctance motors. Through innovative technologies and customized solutions, we can meet the requirements of our customers in various industries. Our motors are characterized by high quality, reliability, and performance.